
Resources
- Agriculture
- Airborne Toxics
- Aircraft & Airports
- (-)Air Pollution
- (-)Air Quality Monitoring
- Air Quality Plans
- Biking & Walking
- California is Going Zero Emissions
- California Public Workshop: Potential Amendments to the Cap-and-Trade Regulation
- Clean Cars
- Climate Change
- Communities
- Construction & Earthmoving Equipment
- Consumer Products
- Energy
- Enforcement
- Environmental Justice
- Freight & Goods Movement
- Fuels
- Health
- Incentives
- Individual Funding Incentives Template
- Indoor Air Quality & Exposure
- Industry & Manufacturing
- Lawn, Garden & Landscape Equipment
- Oceangoing Vessels & Harbor Craft
- On-Road Heavy-Duty Vehicles
- Power Equipment
- Recreational Vehicles & Watercraft
- (-)Research
- Simple Solutions to Improve Air Quality
- Smoke
- Sustainable Communities
- Trains & Railyards
- Transit
- Truck & Bus
- VW Diesel Vehicles
- Zero-Emission Transportation
- Accessible Clean Transportation Options SB 350
- Advanced Clean Cars Program
- Advanced Clean Fleets
- Advanced Clean Trucks
- Agricultural & Prescribed Burning
- Agricultural Burning
- Air Cleaners & Ozone Generating Products
- Air Pollution Complaints
- Air Quality Improvement Program Guidelines
- Air Toxics Program
- Alternative Diesel Fuels
- Ambient Air Monitoring - Regulatory
- California Climate Investments
- Carl Moyer Memorial Air Quality Standards Attainment Program
- Children's Health
- Clean Cars 4 All
- Clean Miles Standard
- Community Air
- Community Air Protection Program
- Community Health
- Community Solutions
- Composite Wood Products Airborne Toxic Control Measure
- Consumer Products Program
- Criteria Air Pollutants
- Criteria Pollutant and Toxics Emissions Reporting (CTR)
- Descarbonización de edificios
- Environmental Tobacco Smoke Identified as a Toxic Air Contaminant
- Exposure
- In-Use Off-Road Diesel-Fueled Fleets Regulation
- Incident Air Monitoring
- Indoor Air
- Lower-Emission School Bus Program
- Mobile Source Emissions Research Program
- Natural and Working Lands
- Naturally Occurring Asbestos
- Oil and Natural Gas Production, Processing, and Storage
- Outdoor Air Quality Standards
- Ozone Transport
- People at Risk
- Prescribed Burning
- Quality Assurance
- Research Planning
- Residential Woodsmoke Reduction
- School Buses
- Small Containers of Automotive Refrigerant
- State and Federal Area Designations
- Statewide Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Network
- Study of Neighborhood Air near Petroleum Sources
- Sustainable Communities & Climate Protection Program
- Vapor Recovery
- Vapor Recovery - Overpressure
- Verification Procedure for In-Use Strategies to Control Emissions from Diesel Engines
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) and Formaldehyde
- Wildfires
- Zero-Emission Powertrain Certification
Rulemaking Documents
Below you will find links to the rulemaking documents for the In-Use Off-Road Diesel-Fueled Fleets Regulation corresponding to the appropriate year changes were adopted.
| November 2022 Amendments | Phase out of the oldest and highest-emitting off-road engines from operation, restrict the addition of vehicles with Tier 3 and 4i engines, require contracting entities to obtain and retain a fleet's valid Certificate of Reported Compliance prior to awarding a contract or hiring a fleet, mandate the use of R99 or R100 Renewable Diesel for all fleets, provide voluntary compliance flexibility options for fleets that adopt zero-emission technology, and include additional requirements to increase enforceability, provide clarity, and provide additional flexibility for permanent low-use vehicles. |
| December 2010 Amendments | Delayed the initial compliance date for all fleets by four years, provided a path to compliance without any required retrofits, and simplify the regulation. |
| July 2009 Amendments | Amendments were approved to provide additional incentives to spur early actions by fleets to reduce emissions, and to make several minor clarifications to the regulation. |
| January 2009 Amendments | Extended the deadline for receiving double credits for early installation of particulate matter retrofits, modify the changing-fleet-size requirements, clarify all sellers of off-road vehicles must maintain records of the disclosure of applicability. |
| Original Regulation | Regulation adopted to reduce emission of diesel particulate matter and oxides of nitrogen from in-use off-road diesel vehicles operating in California. |
LCTI: Our Community, Our Shuttle
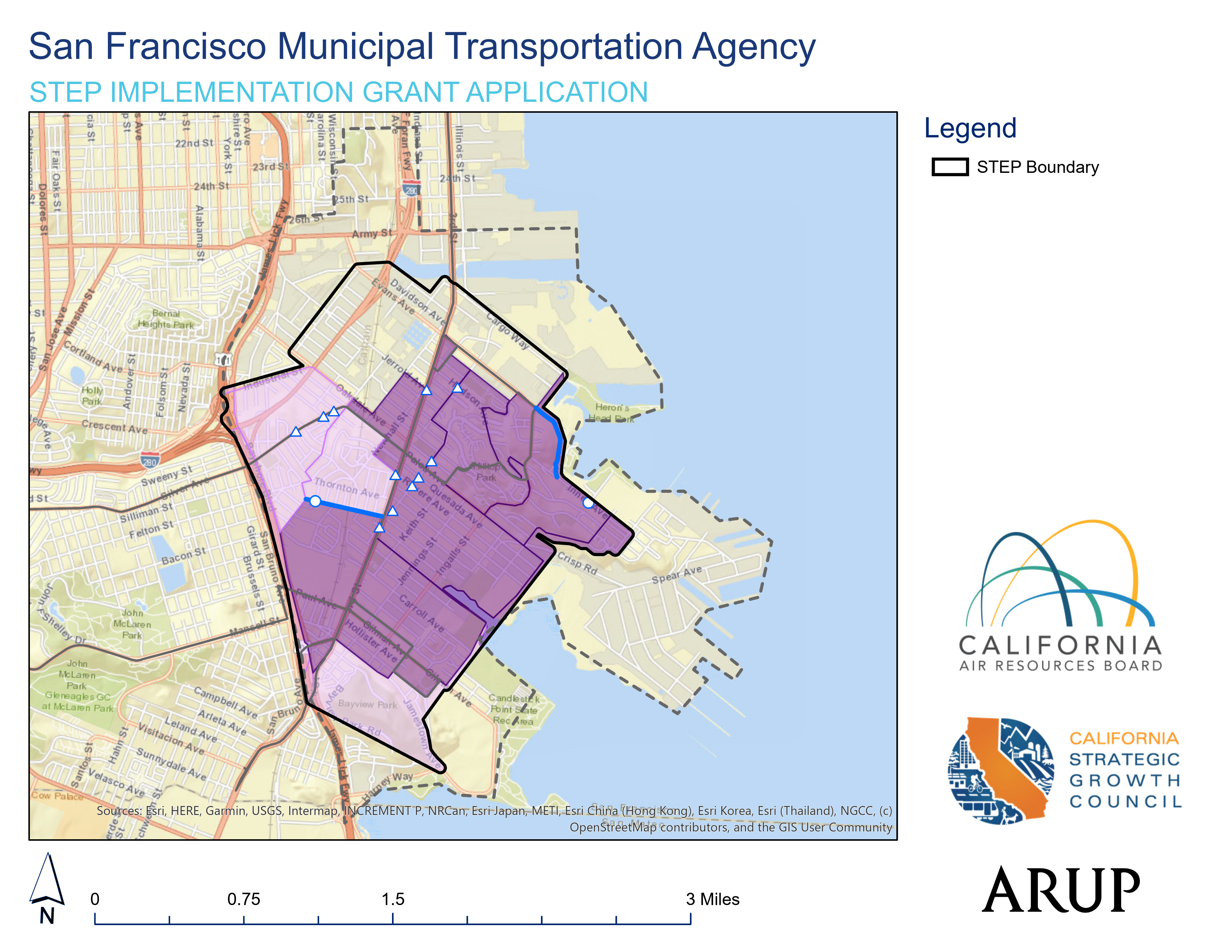
Sustainable Transportation Equity Project (STEP) Implementation Grant
San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency (SFMTA) | Our Community, Our Shuttle: Bayview-Hunters Point Equitable Mobility
June 2022 – March 2026
Project Details
Our Community, Our Shuttle includes a zero-emission, on-demand, and dynamic shuttle service in the Bayview Hunters Point neighborhood. SFMTA will augment this new shuttle service, working with partners to: install a series of pedestrian and transit safety and accessibility improvements identified through the Bayview Community-based Transportation Plan, recruit and train shuttle drivers from within the community in coordination with the CityDrive workforce program, and run a transportation resource center to answer transportation-related questions and connect residents with transportation services and subsidies. All project elements will include extensive outreach and public engagement, including oversight from a Community Congress.
Funding Details
Grant Amount: $10,569,100
Resource Contributions: $3,477,200
Project Total: $14,046,300
By the Numbers
Services, Vehicles & Equipment Funded
- 6 zero-emission shuttles
- About 50 community engagement events planned
- 5.6 miles of bike lane/sidewalks
- Up to 9 pedestrian bulb-out projects
- 2 quick-build active transportation projects
- Shuttle driver trainings completed for 20-30 participants annually
- 0.6 full-time equivalent Transportation Liaison at the Transportation Resource Center
- 6 Transportation Resource Center Youth Champions supporting the Transportation Resource Center
- 10 Community Congress meetings, convening 15 community delegates
Estimated Quantifiable Benefits
- GHG emission reductions: 473 MTCO2e
- NOx reductions: 143 lbs
- PM2.5 reductions: 31 lbs
- ROG reductions: 36 lbs
- Passenger VMT reductions: 1,759,709 miles
- Travel cost savings: $800,668
- Transportation fossil fuel reductions: 35,450 gallons
- Direct Jobs: 127
- Indirect Jobs: 24
- Induced Jobs: 40



Community Details
The project focuses on the Bayview-Hunters Point neighborhood of San Francisco. Bayview-Hunters Point is a resilient and culturally rich community in the southeast of San Francisco with a long history of successful environmental justice advocacy. One of the historical centers of the City’s African American community, Bayview is now a majority Asian, African American, and Hispanic/Latinx community with a high percentage of limited English speakers. Almost half of residents live below 200% of the federal poverty level, with a high concentration of very low-income households in redeveloped public housing, or HOPESF sites, that are in geographically isolated areas and have limited access to the city’s Muni transportation system. 21% of residents do not own a car, with the highest concentrations of car-free households in HOPESF housing. 3.4 miles of streets in the STEP Community are designated on the City's High Injury Network; almost all of these high-injury streets are located on major transit corridors with critical community destinations or in close proximity to HOPESF affordable housing sites.
Demographics of Community Served by Project
36% Asian, 26% Black or African American, 24% Hispanic/Latino, 9% White, Other 8%
Median Household Income: $56,724
Community Benefits
This project intends to co-create services that directly address mobility gaps for Bayview-Hunters Point residents, paving the way for an equitable transportation network. The project will take a people-first approach that is restorative and embedded within community context and culture, intended to:
- Increase mobility and choice for those most vulnerable to transportation challenges
- Generate holistic environmental and socio-economic benefits through the provision of sustainable and accessible zero-emissions transportation alternatives, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and greater access to critical community-serving destinations
- Seek to repair harm, incorporate restorative measures, and utilize lessons from the past to design a better future
- Deliver culturally relevant solutions that are embedded within community context
- Center community decision-making and ownership of data
- Ensure investment and accountability from local leadership that parallels community contributions
Outreach & Engagement Strategies
- Surveys
- Pop-up events
- Focus groups
- Project demonstrations
- Community meetings
- Work groups
- Flyers and brochures
Target Populations
- Youth
- Seniors
- Residents with a disability
- Residents with limited English proficiency
- Residents in affordable housing
Partnership Structure
Grantee
The San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency (SFMTA) is a department of the City and County of San Francisco responsible for the management of all ground transportation in the city. The SFMTA has oversight over the Municipal Railway (Muni) public transit, as well as bicycling, paratransit, parking, traffic, walking, and taxis, creating transportation options that are constant, practical and everywhere and connecting people with their community to enhance the economy, environment and quality of life.
Subgrantees
- A. Philip Randolph Institute San Francisco
- Young Community Developers
- Community Youth Center
- Bayview Hunters Point Community Advocates
- Mission Neighborhood Centers
- Hunters Point Family
- Amplify Impact
- Bay Area Community Resources
- Office of Economic and Workforce Development
- San Francisco Arts & Cultural District
Community Partners
- Rafiki Coalition
- Bayview Hunters Point YMCA
- BMAGIC
- Hunters Point Shipyard Citizen Advisory Committee
- Wu Yee Children's Services
- Southeast Community Facility Commission
- San Francisco Recreation and Parks
- Economic Development on Third
- Social & Environmental Justice Committee SEIU 1021
- Bayview Hunter's Point Citizen Advisory Committee
Contact
Robert Lim | (415) 646-2403 | SFMTA
Public Comment on Application for Variance from the Prohibitions on Use of Certain Hydrofluorocarbons in Stationary Refrigeration, Stationary Air-Conditioning, and Other End-Uses (Cal. Code of Regs., tit. 17, § 95371 et seq.)
Variance Applicant: LG Electronics Inc. (LG)
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) invites interested parties to submit comments on LG's application for a variance. All comments will be publicly accessible via this docket to support an inclusive and transparent process.
LG submitted an application, pursuant to section 95378 of the HFC Regulation, for a variance from the requirements of section 95374(c). Specifically, section 95374(c) prohibits the use of HFCs with a GWP of 750 or greater in new residential dehumidifiers. LG is requesting an impossibility variance to continue the use of R-410A until June 2024.
A copy of the variance application is available on CARB’s website at [https://ww2.arb.ca.gov/our-work/programs/california-significant-new-alternatives-policy-snap/variances/applications]. Please contact the HFC team if you have any questions or concerns: HFCReduction@arb.ca.gov.
Featured
Diesel truck information
Buying guide for clean and efficient vehicles
Air quality in your neighborhood




